Introduction to PaaS
In the dynamic landscape of cloud computing, businesses are increasingly turning to innovative solutions that empower them to build, deploy, and scale applications efficiently. At the forefront of this technological revolution is Platform as a Service , that is reshaping the way we approach software development. So, let’s begin on a journey into the world of Platform as a Service and explore it features.
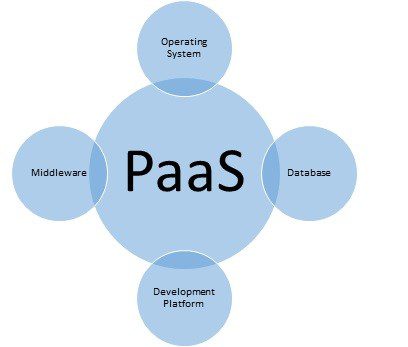
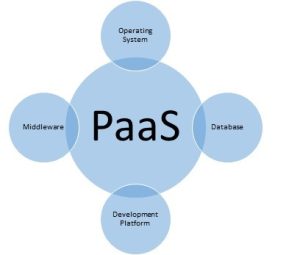
It is one of the of the types of Cloud Computing models. It provides a runtime environment. An external service provider furnishes users with hardware and software tools through online channels. The hardware and software is hosted by the Platform as a Service provider in its infrastructure. These applications are available for purchase from a cloud service provider, and you can access them by paying based on your usage, using an internet connection.
Programmers can easily create, test, run, and deploy web applications using Platform as a Service. Platform as a Service encompasses both infrastructure elements (such as servers, storage, and networking) and platform components (including middleware, development tools, database management systems, business intelligence, and others) to facilitate the entire lifecycle of web applications
Advantages of PaaS
Reduced Costs:–
Platform as a Service is a favorable alternative for organizations aiming to lower their existing operational expenses. PaaS eliminates the necessity of building applications from the ground up, thereby decreasing the expenses linked to typical development. Furthermore, PaaS follows a payment model based on actual usage, leading to significant cost savings for users.
Scalability:-
Scalability is provided by default. Applications deployed can accommodate varying user loads, ranging from single users to thousands, without requiring any modifications to the applications.
Latest Updates:-
Platform as a Service specialists consistently handle all essential updates and security patches on your behalf, ensuring your application operates on the most current stack and remains free from security vulnerabilities.
Disadvantages of PaaS
Vendor lock-in :-
Developers must create applications in accordance with the platform offered by the PaaS provider, making the migration of an application to another PaaS vendor potentially challenging.
Security Risks:-
Although PaaS providers ensure the security of the infrastructure and platform, businesses are accountable for securing the applications they develop.
Compatibility Issue :-
Challenges may emerge when integrating PaaS with existing development platforms.
Types of PaaS
Some of the types of PaaS are:-
-
Public PaaS
In public Platform as a Service, users retain control over software deployment, while the cloud provider oversees the delivery of essential IT components required for hosting applications, such as operating systems, databases, servers, and storage system networks. It is best suited for public cloud.
-
Private PaaS
A private Platform as a Service solution seeks to provide the agility found in public Platform as a Service while upholding the security, compliance, advantages, and potentially reduced costs associated with private data centers. Private Platform as a Service empowers developers to deploy and oversee their company’s applications while adhering to rigorous security, privacy, and compliance standards.
-
Hybrid PaaS
By merging public and private Platform as a Service, hybrid PaaS offers businesses the versatility of unlimited capacity from a public PaaS alongside the cost efficiencies and control associated with owning an internal infrastructure in private Platform as a Service.
-
Communication PaaS :-
CPaaS is a cloud-based platform that allows developers to incorporate real-time communications into their applications without requiring backend infrastructure and interfaces. Examples Skype, FaceTime, WhatsApp
-
Mobile PaaS
MPaaS involves utilizing a paid integrated development environment to configure mobile apps
Use Cases
Web Application Development
Platform as a Service is an ideal solution for building and deploying web applications. The platform manages the underlying infrastructure, enabling developers to focus on building feature-rich and responsive applications.
Data analysis
For projects involving large datasets, Platform as a Service offers robust solutions for data processing and analytics. The scalable nature of PaaS makes it ideally suited for handling a variety of data projects.
IoT development
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, Platform as a Service provides a solid foundation for developing and managing IoT applications. The flexibility of the platform is especially useful in handling the diverse and dynamic data generated by IoT devices.
PaaS Providers
- Microsoft Azure App Service:
- Provides a fully managed platform for building, deploying, and scaling web apps.
- Supports various programming languages and frameworks.
- Google App Engine:
- A serverless platform for developing and deploying applications.
- Supports multiple programming languages, auto-scales based on demand.
- Heroku:
- A cloud platform that enables developers to build, deploy, and scale applications effortlessly.
- Supports multiple programming languages and includes a variety of add-ons.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk:
- Allows for easy deployment and scaling of applications developed in Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, or Docker.
- Provides a managed environment with various pre-configured options.
- IBM Cloud Foundry:
- A cloud application platform that provides a runtime and set of services for developers to build, deploy, and scale applications.
- Supports multiple languages and frameworks.
- Red Hat OpenShift:
- An enterprise Kubernetes container platform with full-stack automated operations.
- Supports both traditional and cloud-native applications.
- Oracle Cloud Platform:
- Offers a comprehensive suite of PaaS services for application development, data management, and more.
- Provides a range of services compatible with multiple programming languages.
- Salesforce App Cloud:
- A platform offering a range of tools for building applications without extensive coding.
- Particularly popular for building customer relationship management (CRM) solutions.
- SAP Cloud Platform:
- A platform-as-a-service offering from SAP for developing and deploying applications in the cloud.
- Supports Java, Node.js, and HTML5.
- Pivotal Cloud Foundry:
- An open-source, multi-cloud platform as a service that provides a cloud-native application runtime.
- Focuses on enabling developers to rapidly build, deploy, and scale applications.
Before choosing a PaaS provider, it’s essential to consider your specific requirements, the programming languages and frameworks your team uses, as well as the level of control and customization you need for your applications. Always check for the latest offerings and features provided by each PaaS provider, as the industry is continually evolving.
Embrace the future of Platform as a Service
In conclusion, Platform as a Service emerges as a game-changer in the realm of cloud computing. By offering a simplified, cost-effective, and scalable development environment, PaaS empowers businesses to innovate and respond rapidly to market demands.
Whether you are a startup aiming to establish a strong digital presence or an established enterprise seeking to modernize your IT infrastructure, Platform as a Service opens up new possibilities. Embrace the power of Platform as a Service and embark on a journey towards a more efficient and agile future.
Looking for IT courses in Pune? Java by Kiran Academy offers flexible options including Java, Python training in Pune, .NET, Testing classes in Pune, MEAN, MERN, and more. Join us for offline or online classes tailored to your convenience.